If you want a healthy and secure business, you must maintain it year round. You may be asking what that means… How do I test my security controls? When should I perform testing? How often should I perform testing? What types of testing should I perform?
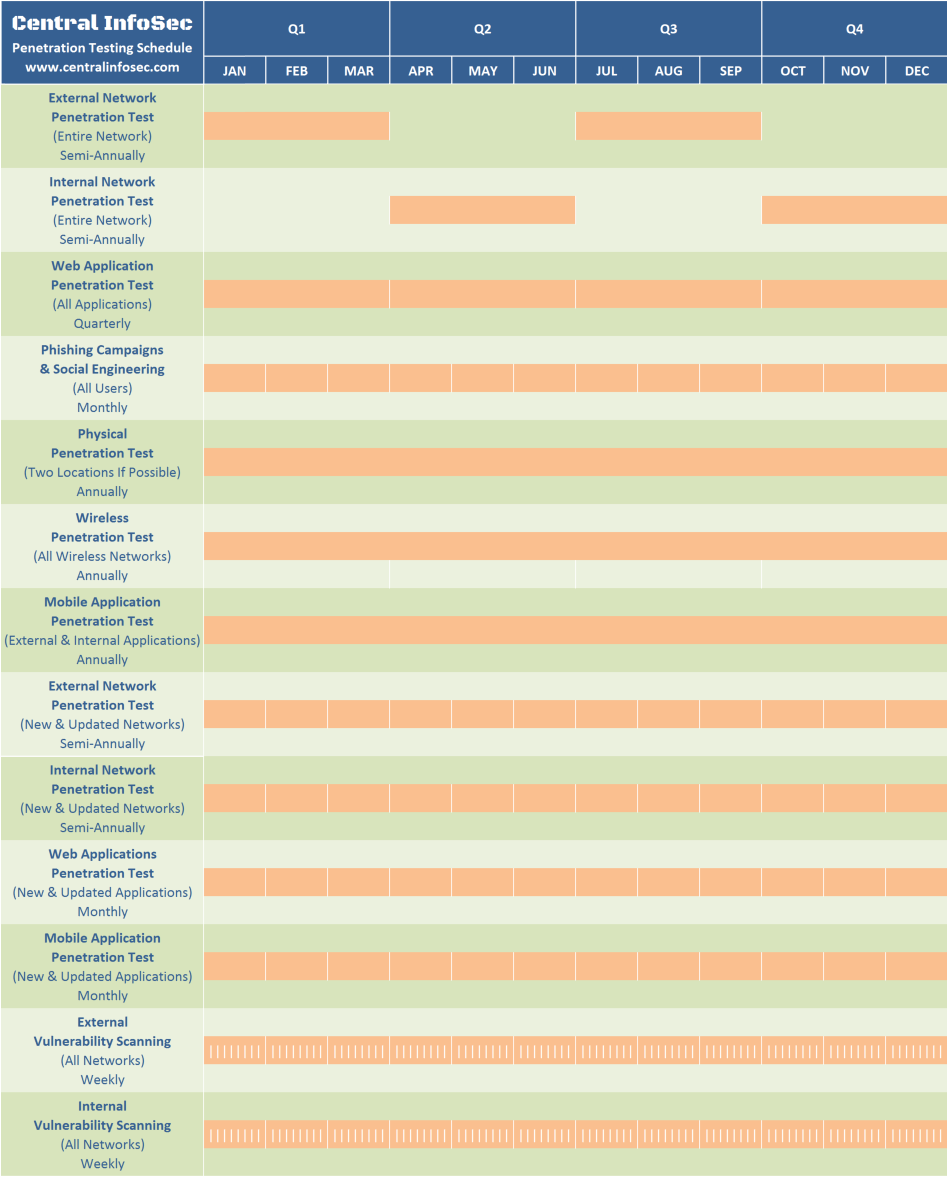
We are hoping to answer all of these questions, plus more, by providing you with a FREE penetration testing schedule to help your business maintain a healthy security posture. This penetration testing schedule was designed so that it can be followed by many organizations of various sizes. If your organization has smaller networks, few web applications, few or no mobile applications, and one physical location, you may consider cutting the testing schedule in half to better support business operations, budgets, and other needs.
What Is A Penetration Test?
Pentesting is a type of security testing that identifies vulnerabilities, threats, and risks in networks, systems, and applications. While vulnerability scanning attempts to identify known vulnerabilities, penetration tests are intended to exploit the weaknesses to gain full situational awareness when it comes to cybersecurity including organizational risk, threats, vulnerabilities, and potential business impact.
Why Do I Need A Penetration Test?
Pentesting can evaluate your security controls and provide you with recommendations to enhance your overall security posture. Pentesting can include real-world security tests using advanced hacking methods to help you identify your weaknesses and improve your security posture. Advanced penetration tests can also simulate attacks on your network using similar techniques as malicious attackers to see if you can identify active attacks!
Pentesting Is Required for Regulatory & Compliance Standards
Pentesting is required for regulatory and compliance standards. These include Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), HITRUST, Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP), Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC), International Organization for Standardization (ISO), Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX), National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and many others.
Why You Need Independent Security Testing
Organizations benefit from independent security testing. Not every business has their own internal team of security professionals, and even those that do, could benefit from a fresh set of eyes. Routine penetration tests can help identify your vulnerabilities, help determine the exploitability of vulnerabilities, help gauge the potential impact of vulnerabilities, help access organization risk, help prioritize your remediation efforts, help you meet regulatory and compliance standards, help you explain security concerns to technical engineers and application developers, and help you justify security-related initiatives to executive leadership.
How Often Do I Need Security Testing?
There is no magic number that fits every organization. Routine pentesting should be performed to identify potential security vulnerabilities. Annual external and annual internal penetration tests are not enough. Monthly or quarterly penetration tests, along with weekly vulnerability scanning are much more effective at improving your overall security posture. Pentesting should also be performed after network changes, application updates, and when new systems are brought onto the network.
Automated Vulnerability Scanning vs Manual Pentesting
While vulnerability scanning may be included in the initial phase of vulnerability identification, manual analysis and manual testing is a must. Vulnerability scanners alone can often miss vulnerabilities, report false positives, or not give accurate risk ratings. Manual pentesting includes additional techniques to identify vulnerabilities along with human analysis to gauge the true severity, potential impact, and organizational risk.
Running a vulnerability scan and saying you may be vulnerable is completely different than actually exploiting vulnerabilities. If you hire a firm that relies on automatic vulnerabilities scanners, critical vulnerabilities could be missed. Central InfoSec team members have published custom tools to track manually found findings that scanners miss.
Areas That Should Receive Pentesting
The following areas at a minimum should receive routine pentesting:
- External Network Pentesting
- Internal Network Pentesting
- External Web Application Pentesting
- Internal Web Application Pentesting
- External Mobile Application Pentesting
- Internal Mobile Application Pentesting
- Physical Pentesting
- Wireless Pentesting
- Social Engineering Pentesting
Annual Pentesting Schedule